Robotic Process Automation (RPA) thrives on speed, efficiency, and reliability. However, many bots require utility functions that are not natively supported, such as generating TOTP tokens, signing JWTs, or performing encoding and decoding operations. Traditionally, these tasks either rely on external APIs or complex embedded scripts, which can be challenging to maintain or scale.
What we'll cover in this article: We’ll explore a lightweight and secure solution: running a Windows Service on each RPA desktop that exposes REST endpoints via localhost. Bots can consume these endpoints as standard APIs while keeping all sensitive operations local.
Why should you extend MuleSoft RPA with custom functions?
MuleSoft RPA provides strong automation capabilities, but certain enterprise workflows require additional cryptographic or authentication operations. Examples include:
- Generating time-based one-time passwords (TOTP) for multi-factor authentication
- Signing JSON Web Tokens (JWT) for secure API communication
- Utility transformations like Base64 encoding or hashing
| Functionality | Purpose | Why local service? |
| JWT generation | Securely create JSON Web Tokens for API authentication. | Ensures sensitive signing keys remain on the local machine while providing reusable token generation for multiple bots. |
| TOTP generation | Generate time-based one-time passwords (2FA). | Enables RPA bots to dynamically authenticate with services requiring MFA without external dependencies. |
| Encryption/Decryption | Protect sensitive data before transmission or storage. | Allows standardized, secure cryptographic operations across bots in a controlled environment. |
| Custom hashing (with private keys) | Generate application-specific or advanced hashes. | Provides a consistent, secure way to produce hashes using approved algorithms across automation workflows. |
Embedding this functionality in every bot can lead to duplication and increased maintenance. A centralized, service-based approach ensures consistency, easier updates, and secure execution across all bots.
Overview of the Windows Service approach
The proposed framework uses a Windows Service that runs locally on each RPA desktop and exposes REST endpoints accessible only on localhost.
Key design points:
- Local-only access: The REST service listens on localhost and firewall rules prevent external access
- Stateless operations: No sensitive data is persisted; all secrets are passed securely at runtime
- Secure credential management: Secrets and keys are stored in MuleSoft RPA Manager’s credentials vault or equivalent
- No network exposure: Tokens and sensitive data are never transmitted over internal or external networks
- Maintainability: Modular design makes it easy to add new algorithms over time
- Scalability: Deployment and updates can be automated using endpoint management tools like BigFix, Intune, or SCCM
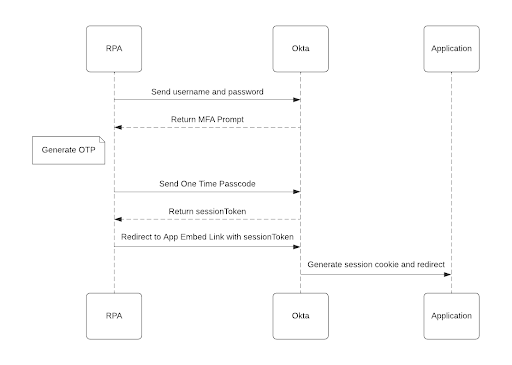
This design keeps token generation secure, manageable, and scalable across the RPA environment.
RPA authentication use case example
Consider a bot that needs to log into an application requiring TOTP-based authentication. Instead of embedding complex logic, the bot calls the local endpoint (e.g. http://localhost:8080/api/gettotp). Then, the Windows Service generates the TOTP using the shared secret stored in RPA Credentials vault. Next, the bot retrieves the token and completes the authentication process.
Benefits include:
- Security: Tokens are never exposed beyond the local machine
- Simplicity: Bots reuse a single, standard API call
- Ability to maintain: Updates are made once at the service level rather than in every bot
Sample implementation snippets
We’ll go over implementation snippets for the following:
- Time-based One-Time Password (TOTP)
- JWT token
- Example requests
TOTP (Time-based One-Time Password)
This endpoint generates a Time-based One-Time Password (TOTP) using the shared secret provided at runtime. Because the service runs locally on each RPA virtual desktop, the generated tokens are never exposed over internal or public networks. Tools like BigFix can be used to securely deploy and maintain the service across multiple client systems.
// Generates a 6-digit TOTP based on a shared secret and current timestamp
[HttpGet("api/gettotp")]
public IHttpActionResult GetTotp([FromUri] string secret)
{
try
{
long currentTimeStep = GetTOTP.GetCurrentTimeStep();
string otp = GetTOTP.GenerateTOTP(secret, currentTimeStep);
return Ok(otp);
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
return BadRequest(ex.Message);
}
} JWT token
This function securely signs a JWT token using a private key stored in a password-protected PKCS#12 keystore. JWT tokens are widely used for OAuth 2.0 assertion flows, allowing MuleSoft RPA bots to authenticate with APIs like Salesforce without exposing sensitive credentials in network traffic.
// Generates a signed JWT assertion using a private key from a secure keystore
public static string GetSignedToken(string keystore, string password, string clientId, string audience, string subject)
{
var header = new { alg = "RS256", typ = "JWT" };
var body = new
{
iss = clientId,
aud = audience,
sub = subject,
exp = DateTimeOffset.UtcNow.ToUnixTimeSeconds() + 180
};
string headerBase64 = Base64UrlEncode(JsonConvert.SerializeObject(header));
string bodyBase64 = Base64UrlEncode(JsonConvert.SerializeObject(body));
string unsignedToken = $"{headerBase64}.{bodyBase64}";
string signature = RSASHA256Sign(keystore, password, unsignedToken);
return $"{unsignedToken}.{Base64UrlEncode(signature)}";
}
Generating JWT (JSON Web Token)Example requests
# Request TOTP
curl -X GET "http://localhost:8080/api/gettotp?secret=<yoursecretkey>"
# Request JWT
curl -X POST http://localhost:8080/api/getjwt \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-d '{
"Keystore": "<Base64EncodedKeystore>",
"KeystorePassword": "password",
"ClientId": "<Client_ID>",
"AudienceURL": "https://yourorg.com",
"Subject": "botuser@example.com"
}'Maintenance and scalability best practices
- Limit exposure: Keep services restricted to localhost
- No persistence: Avoid storing secrets on disk; pass inputs at runtime only
- Vault integration: Use MuleSoft RPA Manager’s credentials vault or equivalent
- Endpoint automation: Deploy and update services via tools like BigFix, Intune, or SCCM
- No network leakage: Tokens never leave the local machine, ensuring security
- Extensibility: Add new functions modularly without impacting existing services
The Windows Service approach is your key to success
A lightweight Windows Service enables secure, maintainable, and scalable custom functions for MuleSoft RPA. From TOTP generation to JWT signing and utility transformations, this approach centralizes functionality, reduces duplication, and keeps sensitive operations confined to the endpoint.
By combining MuleSoft RPA’s automation capabilities with a local service-based framework, organizations can confidently scale their automation while maintaining robust security and operational efficiency.









