It’s common these days for digital transformation projects for lines-of-business teams to require integration. These folks tend to be less technical but have projects, such as creating an omnichannel experience, that requires data from backend systems to be unlocked. These people can struggle to integrate their legacy systems that don’t have APIs or lack visibility into what APIs are available for the endpoints they need to connect to get the job done.
These people go by many names — you can call them shadow IT or citizen integrators — this simply means someone outside of IT who needs to perform an integration as part of their business unit’s digital transformation. Because of the IT delivery gap, the people in these roles are stuck looking for other approaches to get these integration projects done without being held up by IT.
How RPA addresses the integration barriers
According to a survey by Ancoris and the Cloud Industry Forum (CIF), the COVID-19 pandemic has accelerated the pace of digital transformation for many organizations more important than ever. Often, the first key challenge organizations need to address on their digital transformation journey is integration (which if held hostage by IT) can lead to major bottlenecks and stalled digital transformation initiatives. Organizations must empower the existing workforce — the citizen integrators within the business — to address these integration challenges.
As the demand for improved productivity and the need to enable citizen integrators grows, technology such as RPA (robotic process automation) has emerged to fill in the gaps. RPA combines some of the leading aspects of software development today: robots and automation. RPA is a method of automation that enables software with the ability to record a user’s repetitive tasks on their desktop or laptop and can generate a script and perform the task in the same way so that a software robot can automatically perform some of those tasks.
According to Gartner, digital transformation efforts drive RPA adoption, especially for situations like those mentioned above. Such organizations adopting RPA traditionally have many legacy systems and choose RPA solutions to ensure integration functionality.
Enabling citizen integrators with RPA tools
RPA generally provides capabilities to retrieve data from data sources, such as files in excel format or REST APIs and enter them into the graphical user interface (GUI). For example, the terminal of a legacy system or SAPUI of SAP installed in the same machine where the RPA bot is running. Using RPA, citizen integrators can leverage their existing skillsets to enter or retrieve data via the GUI and automate their daily repetitive tasks without getting too technically involved. Additionally, they do not need to study what set of APIs will represent the same tasks they are performing on the GUI especially for SAP. As such, they are more accepting and willing to actively participate in an organization’s digital transformation journey.
The solution will not be complete without providing or consuming data the RPA bot requires to consume or provide respectively. This is where MuleSoft fits perfectly to complete the solution. Citizen integrators can search for capabilities (or APIs) they require via Anypoint Exchange. For example, there could be a capability that unlocks data from two or three backend systems via connectors and returns the consolidated data in excel format which is consumable by the RPA bot as shown in the figure below. Vice versa, there could be a capability that consumes an excel provided by RPA bot and pushes the data to the corresponding backend systems.
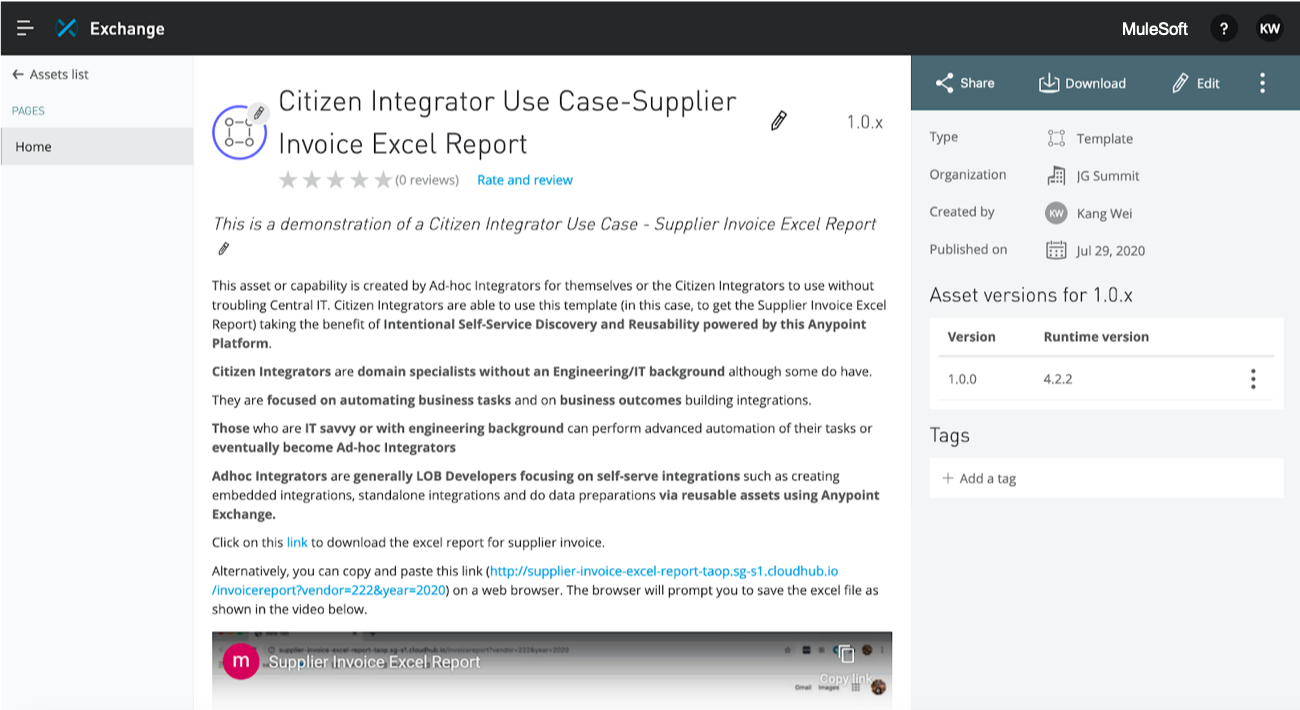
A capability in Exchange that generates an excel report which can be downloaded
Should the capability not be found, citizen integrators can easily build the capability within Anypoint Platform using Flow Designer via click and select approach as shown below.
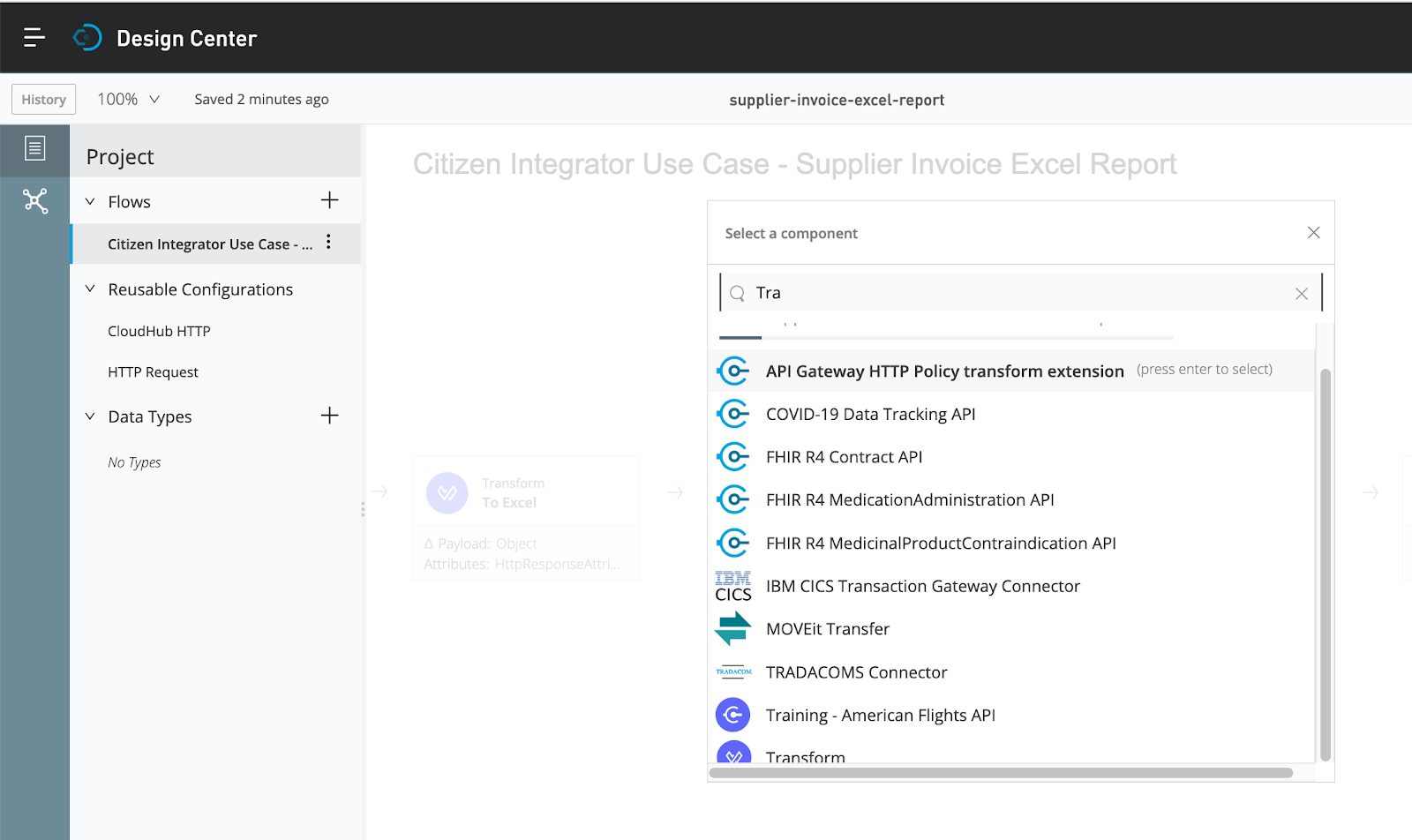
Click and select a component for the flow of excel report generation
Below is the end-to-end illustration for one of the many possibilities on how citizen integrators are empowered to perform integrations with APIs and RPA mentioned above.
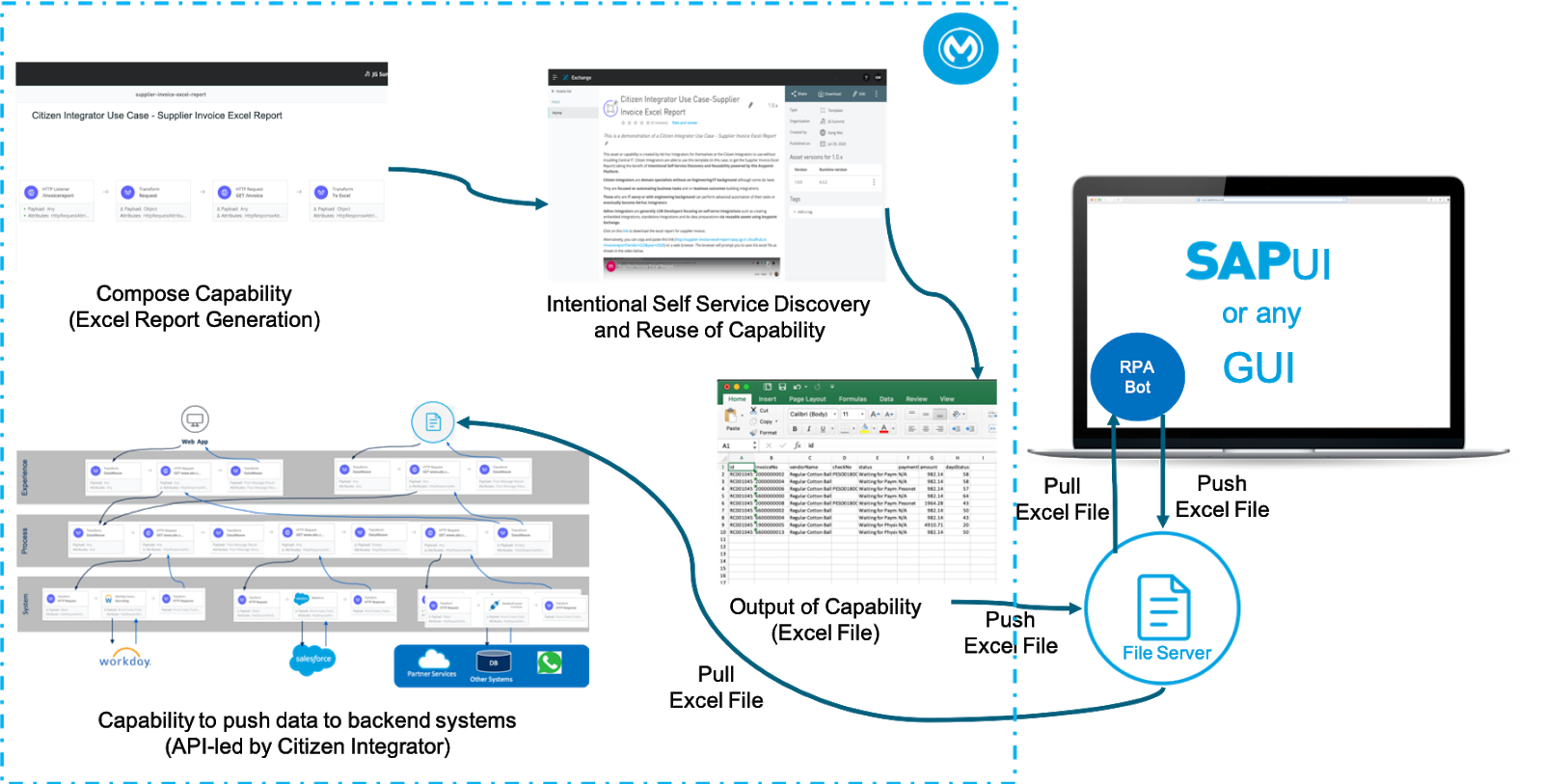
End-to-end illustration of an example showcasing how citizen integrators are empowered to perform integrations with MuleSoft and RPA.
Anypoint Platform empowers citizen integrators to perform server-side integration unconsciously without coding and being too technical through intentional self-service discovery and reuse of capabilities exposed by adhoc integrators or integration specialists in the hybrid integration platform (HIP) ecosystem.
In a Gartner article, traditional integration toolkit — a set of task-specific integration tools — can’t address the complex challenges posed by digital transformation. Organizations need to move toward what Gartner calls a HIP. The HIP is the “home” for all functionalities that ensure the smooth integration of multiple digital transformation initiatives in an organization. MuleSoft’s Anypoint Platform is a complete enterprise HIP supporting the various personas (i.e. the citizen integrator, the integration specialist, and system administrator) in the ecosystem. With it, organizations can address various integration scenarios by adopting an API-led approach that packages underlying connectivity and orchestration services as easily discoverable and reusable building blocks, exposed by APIs. This enables businesses to accelerate their digital transformation journey.
The future of intelligent integration
A Gartner report predicts that citizen integrators constantly seek to perform integration tasks as a whole, and generally do not differentiate the processes of integrating data and applications. As a result, leaders will need to re-evaluate traditional integration practices, their current approach and platform, and explore AI to make things simpler for citizen integrators’ to drive their involvement in closing the IT delivery gap.
MuleSoft has already started to innovate on its product capabilities incorporating AI or related technology making Anypoint Platform an intelligent platform that can perform integration tasks from development to operations. Such capabilities will encourage citizen integrators to perform server-side integration by making integration easier and faster without being technical to achieve their desired outcome and automation of business tasks.
RPA has started to leverage AI technologies such as optical character recognition (OCR), text analytics, and machine learning to improve the experience of the smart workforce. As cognitive AI matures, it will help to take RPA (also known as cognitive RPA) a step further by enabling organizations to automate processes that include unstructured data sources, including scanned documents, emails, letters, and voice recordings. The real power of cognitive RPA is that it empowers citizen integrators to automate more complex, less rule-based tasks on their workstations, desktops, or laptops.
MuleSoft has formed technology partnerships with leading RPA vendors to enable the citizen integrators to innovate at scale. See more details about our RPA partnerships here.









